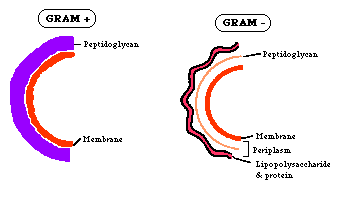

Gram-stains need to be interpreted with some care.
The history of the culture is important in Gram-staining. The age of the culture and the pH of the medium in which the bacteria are grown may affect its reaction to Gram's stain.
Old cultures of Gram-positive organisms and those grown in acid media frequently appear either Gram-negative or Gram-variable.
On the other hand, Gram-negative organisms do not become Gram-positive regardless of age or medium used. Only a fresh cultures should be used for Gram-staining and the presence of a few Gram-negative representatives in a predominantly Gram-positive culture is common.
In spite of these difficulties, the combination of Gram-reaction and cell morphology is a powerful tool in identifying cultivatable bacteria.